Introduction to the ESP32/Grove Ecosystem
Introduction to the ESP32/Grove Ecosystem
The IoT module you use in a smart home setup can vary widely. This is why it is important to understand IoT devices in a general sense; they sense conditions, compare those conditions against set points, and then they send commands if needed. Many also allow for direct user control through an app or interface.
In these lessons, you’ll be using an ESP32 as the heart of two different IoT systems. The name ESP32 refers to a class of low-power microcontrollers developed by a company called Espressif Systems. Seeed Studios has taken an ESP32 and put it on a board with a very small form factor. It is actually smaller than a stamp!
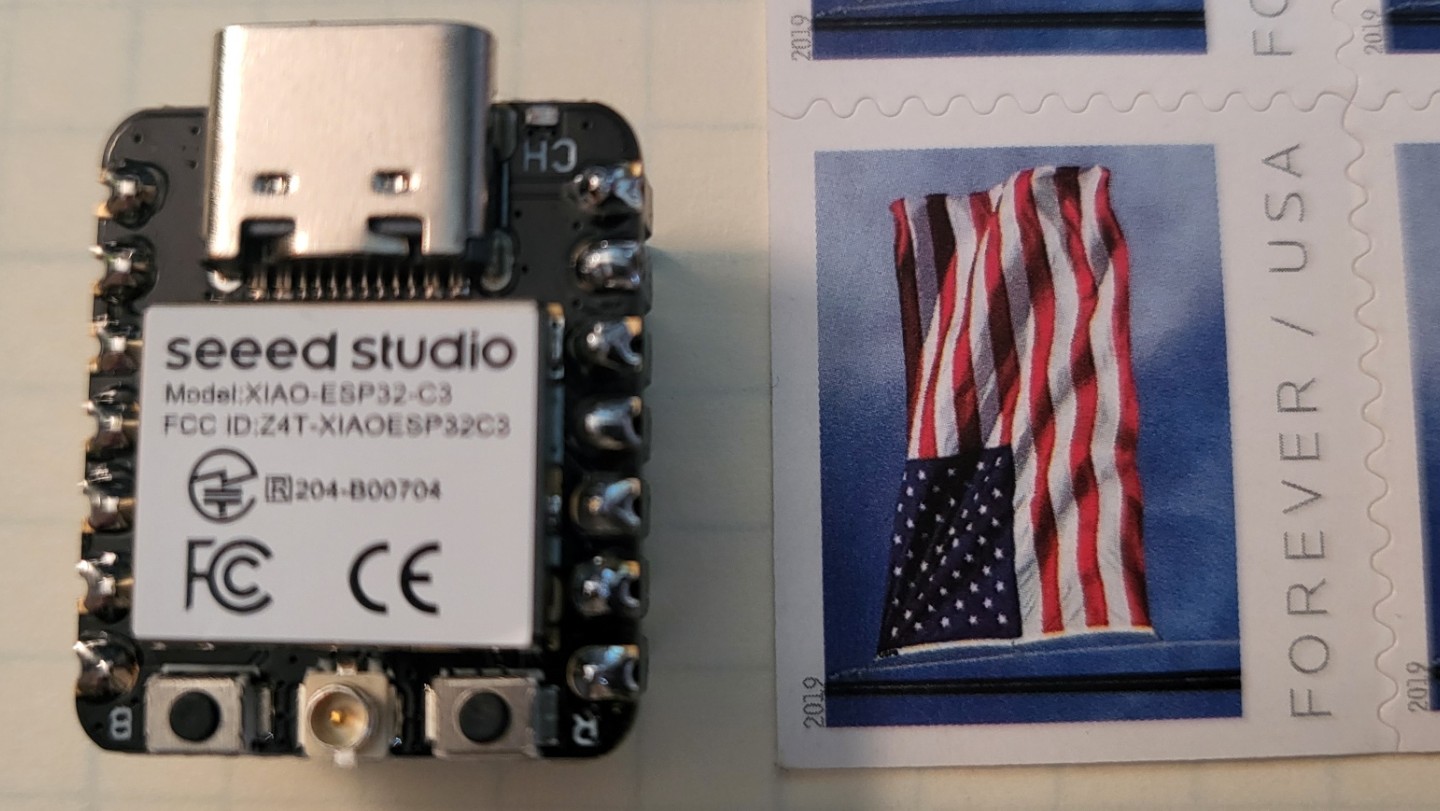
In an electrician's work, you will likely get an out-of-the-box solution that will likely need to be wired into a house’s electrical system and, perhaps, include some devices to connect. Similarly, the ESP32 will use the Grove Ecosystem, which is modular. This means that all of the components can simply plug together rather than having to be soldered. The Grove connectors are designed in a way that they can only fit together in one orientation. If it is not going together easily, DO NOT FORCE IT! Check the two connection points and proceed accordingly.
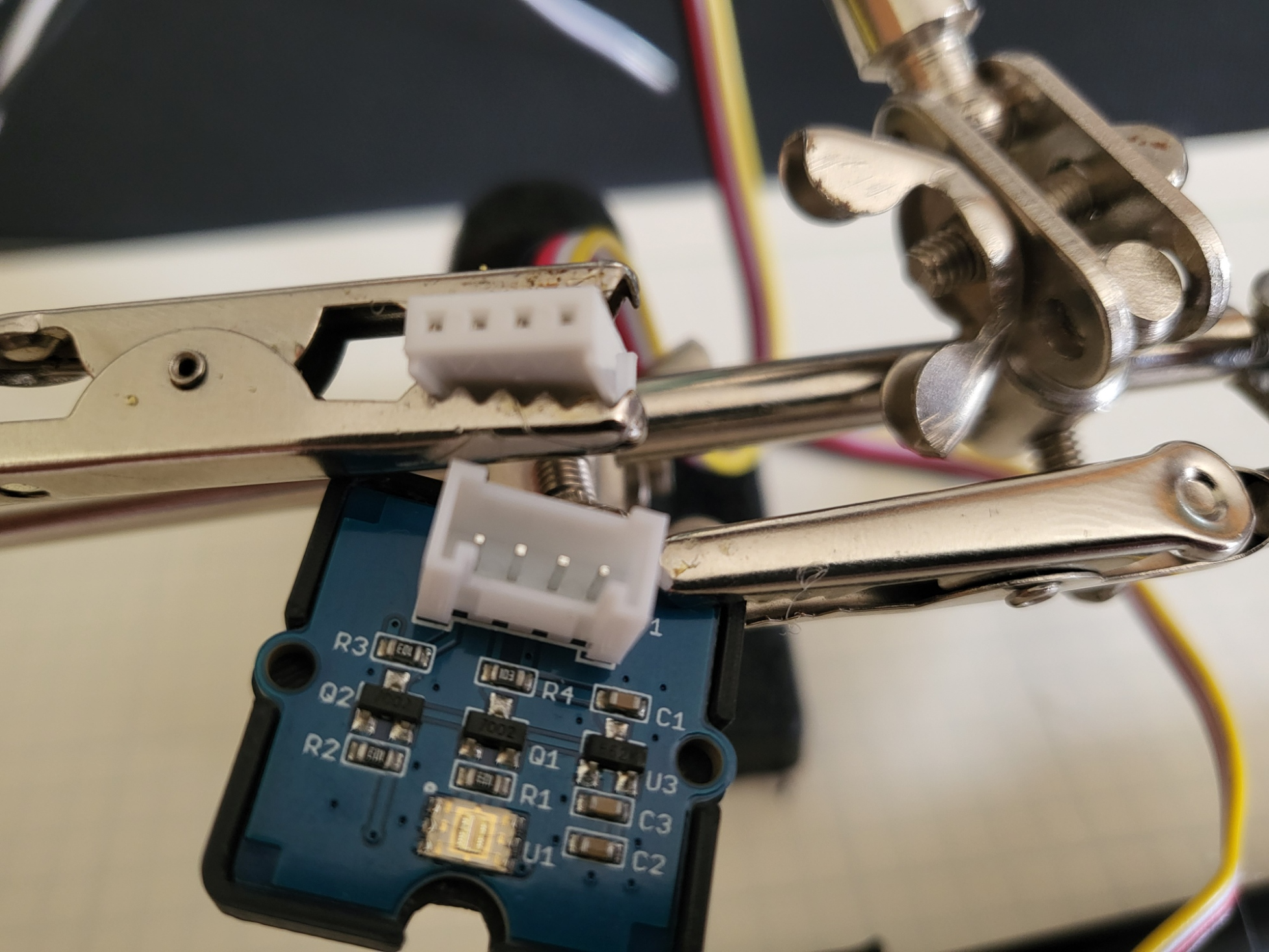
To connect to the sensors, the ESP32 is placed in an expansion board. This board allows Grove components to be easily connected to the system. In the lesson activity, you will see how the ESP32 and Grove components connect to the Click using building block-style stud and tube connectors.